Otoplenie-Blog.com.ua > Bookkeeping > Accrued Rent Accounting under ASC 842 Explained
Accrued Rent Accounting under ASC 842 Explained

For an extensive explanation of prepaid rent and other rent accounting topics, see our blog, Prepaid Rent and Other Rent Accounting for ASC 842 Explained (Base, Accrued, Contingent, and Deferred). Under ASC 842 base rent is included in the establishment of the lease liability and ROU asset. The amortization of the lease liability and the depreciation of the ROU asset are combined to make up the straight-line lease expense. Similarly to ASC 840, this straight-line lease expense is calculated as the sum of all of the rent payments over the lease term and divided by the total number of periods. A full example with journal entries of accounting for an operating lease under ASC 842 can be found here.
Accounting for rent under the new lease accounting standards
On the first day of the next month, the period the rent check was intended for, the prepaid rent asset is reclassed to rent expense. The periodic lease expense for an operating lease under ASC 842 is the product of the total cash payments due for a lease contract divided by the total number of periods in the lease term. If all details of a contract are the same, organizations record the same amount for lease expense under ASC 842 as they would for rent expense under ASC 840. Sometimes a business does not own any specific type of property, plant, and/or machinery. They take the required asset on rent and pay the pre-specified installment for the asset in terms of cash or cheques.
Accounting for accrued rent with journal entries
Introduction to Credit Default Swaps (CDS)A Credit Default Swap (CDS) is a financial derivative that allows an investor to «swap» or offset their credit risk with that of another investor. If all other sites open fine, then please contact the administrator of this website with the following information.
Eliminate Lease Accounting Errors
Rental expenses are a significant cost of doing business, and can vary depending on the type and location of the property. Rent expenses, also known as occupancy costs, cover the cost of occupying a property for business purposes. This expense includes office, retail, storage space, or factory rent. Retail businesses tend to have high rent expenses, in addition to wages and marketing costs.
- A small privately held company, ABC operates several operations, including earthmoving, landscaping and retail, to the general public.
- Additionally, at the time of transition to ASC 842, any outstanding prepaid rent amounts would be included in the calculation of the appropriate ROU asset.
- At transition, any cumulative balances accrued for unpaid rent obligations will be reclassified to the opening balance of the appropriate lease’s ROU asset.
- Hannifin has occupied the building for December; hence, it must realize rent expense for December in its books by making the following accrual entry on December 31, 2020.
- On December 1, 2020, the Hannifin corporation obtains a building on rent to setup a factory in it.
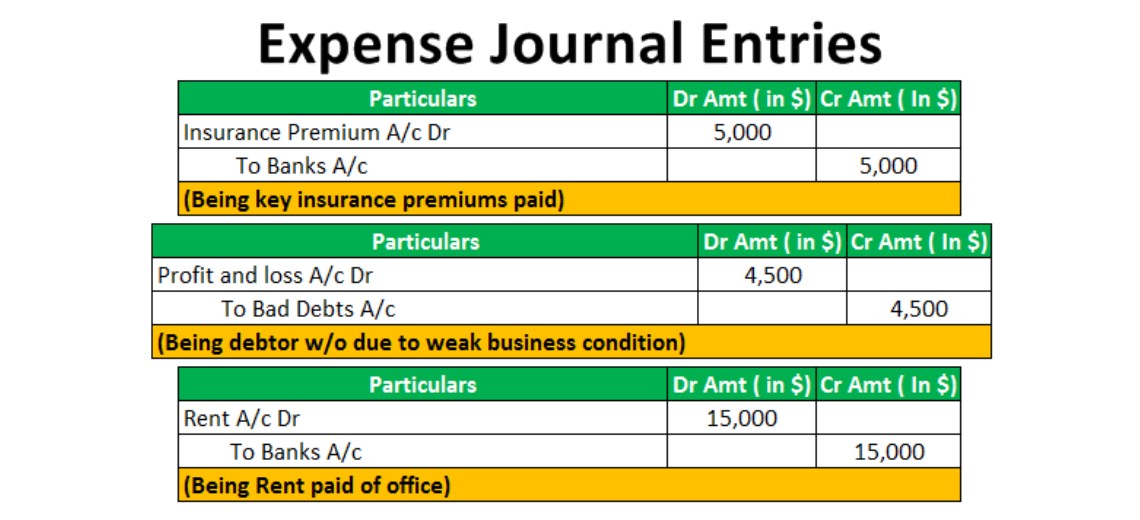
Rent Payable Journal Entry Example
Below is a portion of the amortization schedule for the lease in the example for illustrative purposes. The aggregate payments required under the lease total is $15,767,592. Let’s assume this is an operating lease, and the retailer transitioned to ASC 842 on January 1, 2022 and utilized a 7% borrowing rate for the present value calculation. Record the necessary journal entry for the month ending April 2023.
Deferred rent is a liability account representing the difference between the cash paid for rent expense in a given period and the straight-line rent expense recognized for operating leases under ASC 840. When a rent agreement offers a period of free rent, payments are not due to the lessor or landlord. average property tax However, you are recording the straight-line rent expense calculated by dividing the total amount of required rent payments by the number of periods in the lease term. Additionally, deferred rent is also recorded for lease agreements with escalating or de-escalating payment schedules.
At the month-end, the company needs to record expenses and revenue to prepare a financial statement. So they need to record rental expenses even the payment is not yet made. For those in a hurry, the journal entry debits the rent expense account and credits the bank account.
But for lease accounting, it can make things a little more difficult. Prepaid rent is rent that’s been paid in advance of the period for which it’s due. Under ASC 842, the concept of prepaid rent does not exist; however, in practice it is common for lessees to make rent payments in advance. This means that paying attention to when prepaid rent is paid and ensuring it’s recorded correctly is of paramount importance.
If you don’t like debits and credits, accounting study is going to be very painful. A small privately held company, ABC operates several operations, including earthmoving, landscaping and retail, to the general public. ABC rents storage space for retail business and pays $1,500 a month in advance.
In short, organizations will now have to record both an asset and a liability for their operating leases. Under the old lease accounting rules, the cash payments for operating leases were recorded as rent expense in the period incurred and no impact to the balance sheet was recognized. In conclusion, accounting for rent expense is changing insignificantly from ASC 840 to ASC 842. Now if only the same thing could be said about the accounting for operating leases. Deferred rent is primarily linked to accounting for operating leases under ASC 840. Nevertheless, differences between lease expense and lease payments also exist under ASC 842.
Rent paid journal entry is passed in order to record the necessary rent payments against rented assets. Under ASC 842, accrued rent is no longer recognized as its own line item on the financial statements. Under ASC 840, accounting for rent in operating leases was straightforward.