Otoplenie-Blog.com.ua > Bookkeeping > What is a Liability Account? Definition, Types, and Examples
What is a Liability Account? Definition, Types, and Examples
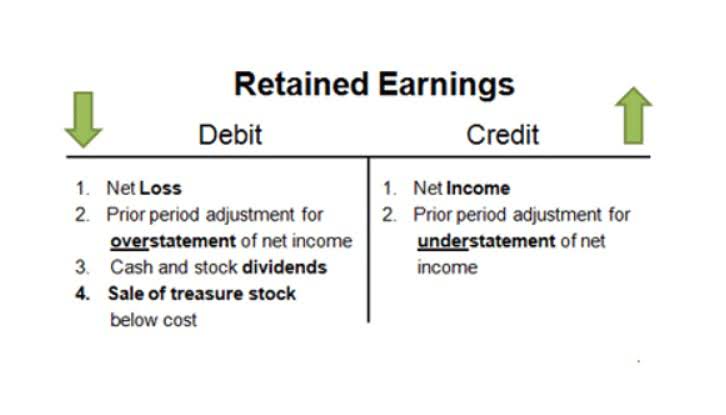
Current liabilities are liabilities owed by a company to a lender for 1 year or less. In the case of non-payment creditors has the authority to claim or confiscate the company’s assets. Even in the case of bankruptcy, creditors have the first claim on assets. This can either be raised through equity (Issuance of shares on the stock exchange) or debt (Obtained from banks or issuance of bonds). Unless there is litigation involving objections to the discharge, the debtor will usually automatically receive a discharge.
- It is assumed that the decrease in the supplies on hand means that the supplies have been used during the current accounting period.
- It involves anticipating future financial obligations and employing strategies to meet them while maintaining solvency.
- For the company’s December income statement to accurately report the company’s profitability, it must include all of the company’s December expenses—not just the expenses that were paid.
- The amount in the Supplies Expense account reports the amounts of supplies that were used during the time interval indicated in the heading of the income statement.
- Liability accounts are categorized on the balance sheet under current liabilities, like short-term loans or unearned revenue, and non-current liabilities, like long-term debt or bonds payable.
- If you want to minimize the number of adjusting journal entries, you could arrange for each period’s expenses to be paid in the period in which they occur.
FAQs On Liabilities In Accounting
The impact of these liabilities can significantly influence a company’s financial statements, making it essential for businesses to monitor, manage and strategically plan their liability structure. Familiarity with these concepts can help stakeholders make informed decisions about a company’s financial well-being and future prospects. By far the most important equation in credit accounting is the debt ratio. It compares your total liabilities to your total assets to tell you how leveraged—or, how burdened by debt—your business is. These are any outstanding bill payments, payables, taxes, unearned revenue, short-term loans or any other kind of short-term financial obligation that your business must pay back within the next 12 months.
What is your current financial priority?

A company with too many liabilities compared to its assets may face cash flow problems or increased financial risk. Understanding a company’s liabilities can also help assess its ability to meet debt obligations and the potential for future growth. Additionally, income taxes payable are classified as a current liability. The amount of taxes a company owes might fluctuate based on its profitability and tax planning strategies. These obligations Bookkeeping for Chiropractors can affect a company’s operating cash flows, as they represent a cash outflow the company will need to satisfy. Lease payments are a common type of other liability in accounting.

Where are Liabilities recorded on a balance sheet?
- The state’s commitment to staying ahead of national trends by updating and adapting its laws to meet the needs of modern businesses has solidified its position as an ideal jurisdiction for setting up a Wyoming LLC.
- We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources.
- The company must recognize a liability because it owes the customer for the goods or services the customer paid for.
- Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications.
- An expense is the cost of operations that a company incurs to generate revenue.
- This flexibility allows businesses to tailor their management approach according to their needs and operational strategies.
Liabilities are categorized as current or non-current depending on their temporality. They can include a future service owed to others such as short- or long-term borrowing from banks, individuals, or other entities or a previous transaction that’s created an unsettled obligation. These debts usually arise what is liability account from business transactions like purchases of goods and services. For example, a business looking to purchase a building will usually take out a mortgage from a bank in order to afford the purchase. The business then owes the bank for the mortgage and contracted interest.

- Each classification on the balance sheet plays a distinct role in financial analysis.
- If the revenues earned are a main activity of the business, they are considered to be operating revenues.
- All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own.
- As in chapter 7, however, discharge may not occur in chapter 13 if the debtor fails to complete a required course on personal financial management.
- Keep up with Michelle’s CPA career — and ultramarathoning endeavors — on LinkedIn.
- The ending balance in Depreciation Expense – Equipment will be closed at the end of the current accounting period and this account will begin the next accounting year with a balance of $0.
- Current liabilities are obligations that a company needs to settle within a year, whereas long-term liabilities extend beyond a year.
It is assumed that the decrease in the amount prepaid was the amount being used or expiring during the current accounting period. The balance in Insurance Expense starts with a zero balance each year and increases during the year as the account is debited. The balance at the end of the accounting year in the asset Prepaid Insurance will carry over to the next accounting year.
- When evaluating the performance of a company, analysts like to see that any short-term liabilities can be completely covered by cash.
- The debtor and the debtor’s attorney also receive copies of the discharge order.
- Some valuable items that cannot be measured and expressed in dollars include the company’s outstanding reputation, its customer base, the value of successful consumer brands, and its management team.
- Accountants realize that if a company has a balance in Notes Payable, the company should be reporting some amount in Interest Expense and in Interest Payable.
- A review of the balance in Unearned Revenues reveals that the company did indeed receive $1,300 from a customer earlier in December.
- “It’s going to be an iterative, recursive process, and it may take up to five years before everybody is on that system and able to report,” he said.
#2 — Non-Current Liabilities

Liabilities are not just about immediate payments; they include economic responsibilities that a company expects to settle in the future, reflecting past transactions and financial activities. In accounting this means to defer or to delay recognizing certain revenues or expenses on the income statement until a later, more appropriate time. Revenues are deferred to a balance sheet liability account until they are earned in a later period. When the revenues are earned they will be moved from the balance sheet account to revenues on the income statement. The accounting method under which revenues are recognized on the income statement when they gross vs net are earned (rather than when the cash is received).